In the previous post we talked about how to create nested paths in NextJS, now let’s discuss how to make dynamic pages.
Next.js is a powerful React framework that simplifies the creation of dynamic and performant web applications. One of its standout features is the ability to generate dynamic pages effortlessly. In this in-depth exploration, we’ll delve into the concepts and provide examples to enhance your understanding of creating dynamic pages in Next.js.
Contents
Understanding Dynamic Pages in Next.js
Dynamic pages in Next.js allow you to generate pages on-the-fly based on data. This is particularly useful when you have content that changes dynamically, such as blog posts, product details, or user profiles. Next.js leverages the concept of “dynamic routes” to achieve this.
Dynamic Routes and File Structure
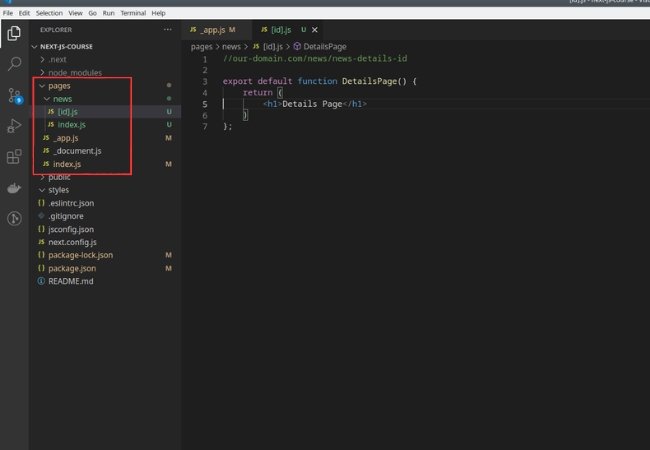
Dynamic routes in Next.js are created by adding square brackets ([]) to the pages in the pages directory. Let’s consider an example where we want to create dynamic pages for individual blog posts.
- File Structure:
pages/ ├── posts/ │ ├── [slug].js │ └── index.js └── index.js
Here,
[slug].jsrepresents our dynamic route for individual blog posts.
- Dynamic Route Component ([slug].js):
// pages/posts/[slug].js import { useRouter } from 'next/router'; const Post = () => { const router = useRouter(); const { slug } = router.query; return ( <div> <h1>Post: {slug}</h1> {/* Fetch and display content for the specific post */} </div> ); }; export default Post;
getStaticPaths and getStaticProps
Next.js provides two key functions, getStaticPaths and getStaticProps, to facilitate the creation of dynamic pages.
getStaticPaths: This function is used to fetch data (like blog post slugs) and generate paths based on that data. It’s crucial for telling Next.js which dynamic routes to pre-render.getStaticProps: This function fetches specific data for a given path. In our example, it fetches the content of a blog post based on its slug.
Generating Dynamic Pages Programmatically
Next.js provides a powerful function called getStaticPaths that allows you to specify dynamic routes based on data. Let’s modify our example to fetch blog post slugs from an API.
- Fetching Data with
getStaticPaths:// pages/posts/[slug].js import { useRouter } from 'next/router'; const Post = ({ postData }) => { const router = useRouter(); const { slug } = router.query; return ( <div> <h1>Post: {slug}</h1> {/* Display content from postData */} </div> ); }; export async function getStaticPaths() { // Fetch blog post slugs from an API const res = await fetch('https://api.example.com/posts'); const posts = await res.json(); // Generate dynamic paths based on the slugs const paths = posts.map((post) => ({ params: { slug: post.slug } })); return { paths, fallback: false }; } export default Post;In this example,
getStaticPathsfetches blog post data and generates paths for each post. - Fetching Data for Each Page with
getStaticProps:// pages/posts/[slug].js import { useRouter } from 'next/router'; const Post = ({ postData }) => { const router = useRouter(); const { slug } = router.query; return ( <div> <h1>Post: {slug}</h1> {/* Display content from postData */} </div> ); }; export async function getStaticPaths() { // Fetch blog post slugs from an API const res = await fetch('https://api.example.com/posts'); const posts = await res.json(); // Generate dynamic paths based on the slugs const paths = posts.map((post) => ({ params: { slug: post.slug } })); return { paths, fallback: false }; } export async function getStaticProps({ params }) { // Fetch data for the specific post using params.slug const res = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/posts/${params.slug}`); const postData = await res.json(); return { props: { postData, }, }; } export default Post;
Conclusion
Creating dynamic pages in Next.js opens up a world of possibilities for building flexible and content-rich applications. By understanding dynamic routes, file structure, and utilizing getStaticPaths and getStaticProps, you can seamlessly integrate dynamic content into your Next.js projects. Experiment with these concepts and take your web development skills to new heights with Next.js!




0 Comments