Contents
Understanding Rebasing:
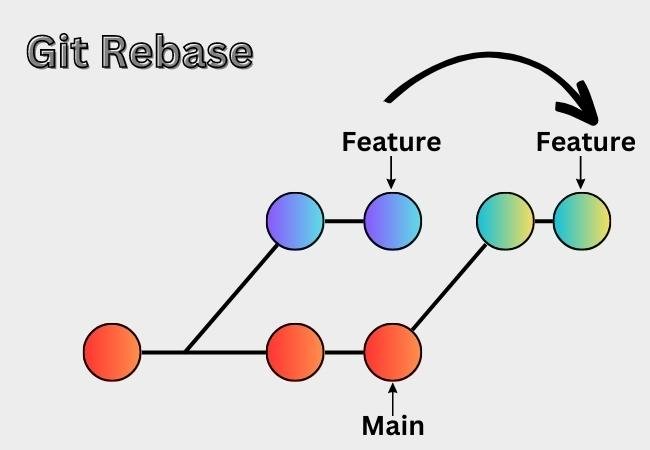
Rebasing is the process of moving, or “replaying,” a series of commits from one branch onto another. It essentially allows you to incorporate changes from one branch onto another while maintaining a cleaner and more linear commit history.
Benefits of Rebasing:
Rebasing offers several advantages:
- A cleaner commit history with a linear progression of changes.
- Easier identification of when a feature or bug fix was introduced.
- Helps avoid merge commits, making the history more readable.
- Facilitates smoother integration of changes from a feature branch into the main branch.
Prerequisites:
Before you start rebasing, make sure you have a good understanding of Git basics. You should also have Git installed on your system and a Git repository set up.
Step-by-Step Guide to Rebasing:
Rebasing onto the Upstream Branch:
- Ensure your working directory is clean and up to date:
git status,git pull. - Checkout the branch you want to rebase onto:
git checkout main. - Start the rebase:
git rebase feature-branch.
Resolving Conflicts:
- If conflicts arise during the rebase, Git will pause the process.
- Open the files with conflicts, resolve the issues, and save the changes.
- Stage the resolved files:
git add resolved-file. - Continue the rebase:
git rebase --continue.
Completing the Rebase:
- After resolving all conflicts, the rebase will complete.
- Verify that everything looks as expected.
- Force push the rebased branch:
git push origin feature-branch --force.
Interactive Rebasing:
Interactive rebasing allows you to modify commits during the rebase process. To start interactive rebasing, use: git rebase -i commit-hash^.
Rebasing Considerations:
- Only rebase local, unpublished branches: Rebasing should be reserved for branches that have not been pushed to a shared repository.
- Collaboration: Communicate with your team before rebasing to avoid conflicts and ensure everyone is on the same page.
- Backup: If unsure, create a backup branch before rebasing to have a fallback option.
Conclusion:
Rebasing is a powerful technique that enhances your Git workflow by creating a more organized commit history.
By following the steps outlined in this tutorial, you can confidently rebase your branches, integrate changes, and maintain a cleaner version control history in your Git projects.
Remember, practice makes perfect. Feel free to experiment with rebasing in a safe environment to gain a deeper understanding of how it works.
Happy coding!





0 Comments