When using Git, a crucial tool for tracking changes in your project, handling branches is a key aspect of the development process. As your project gets bigger, it becomes crucial to know all the branches, both on your computer and on the online repository.
In this blog post, we’ll look at different Git commands that help you easily see and understand the names of all the branches, whether they are on your computer or stored online. Learning these commands will make it easier for you to move around and control branches in your Git projects.
Contents
Git – Listing Local Branches
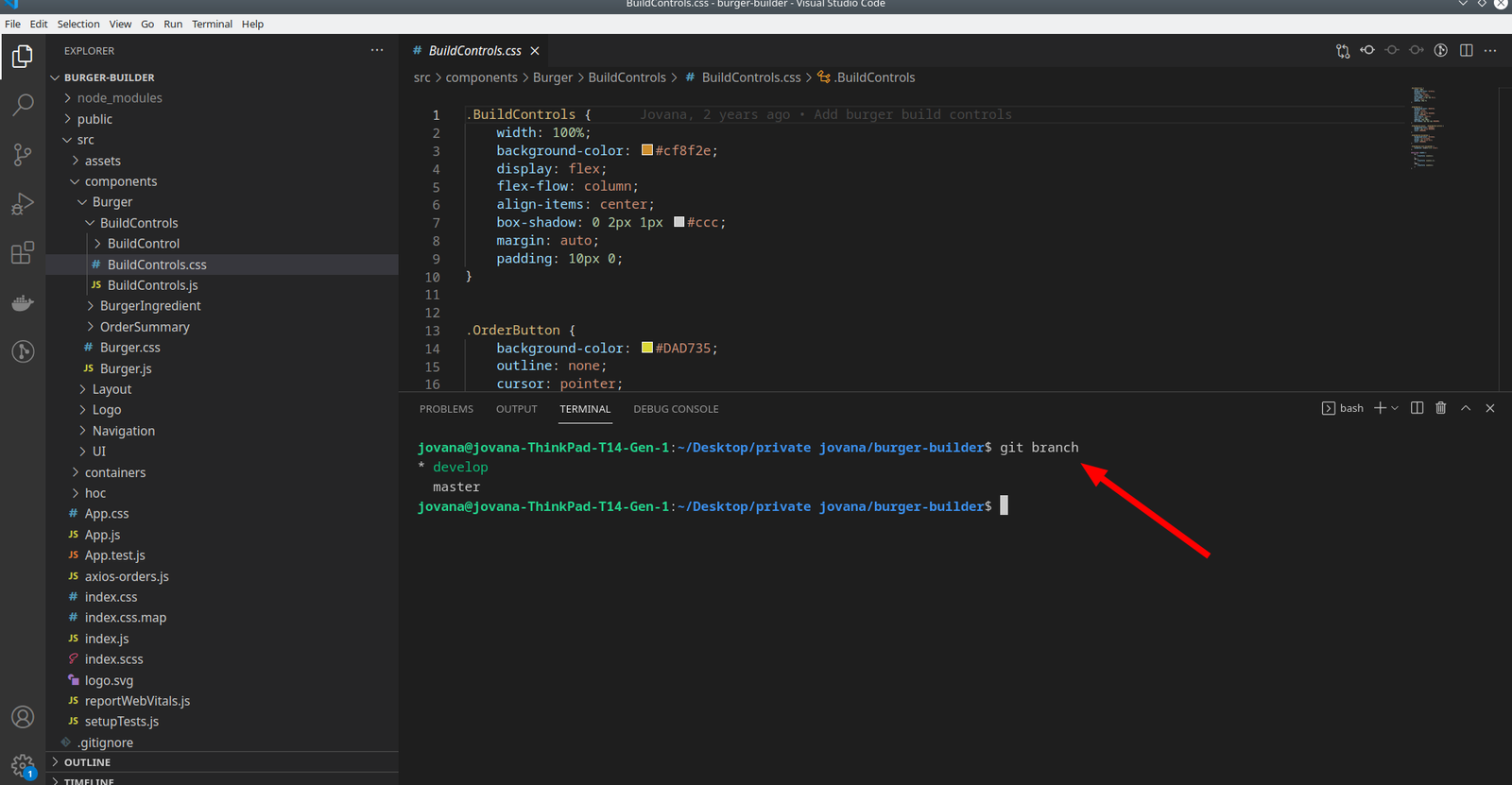
To display all local branches in your Git repository, open your terminal and use the following command:
git branch
This command will show a list of branches with an asterisk (*) next to the currently checked out branch. The branch names will be listed in alphabetical order.
Showing Remote Branches
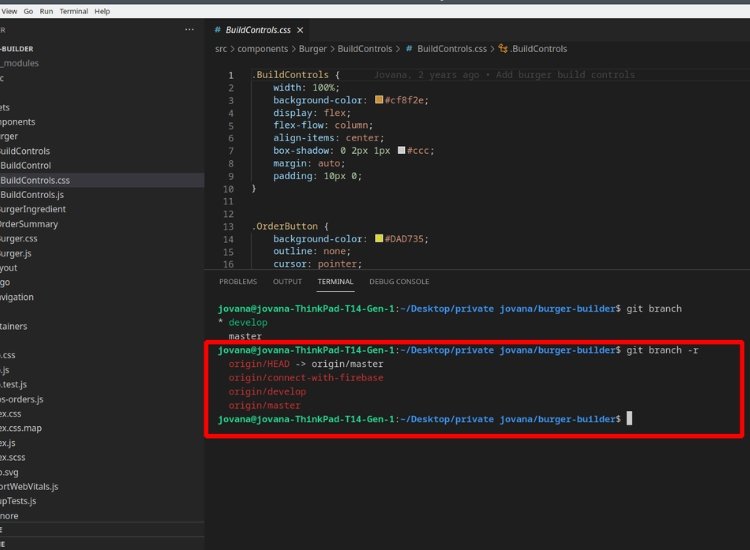
To view all remote branches in your Git repository, execute the following command:
git branch -r
This command displays a list of remote branches, which are branches that exist on the remote server. Remote branches are prefixed with the name of the remote repository, such as “origin/”.
Displaying All Branches
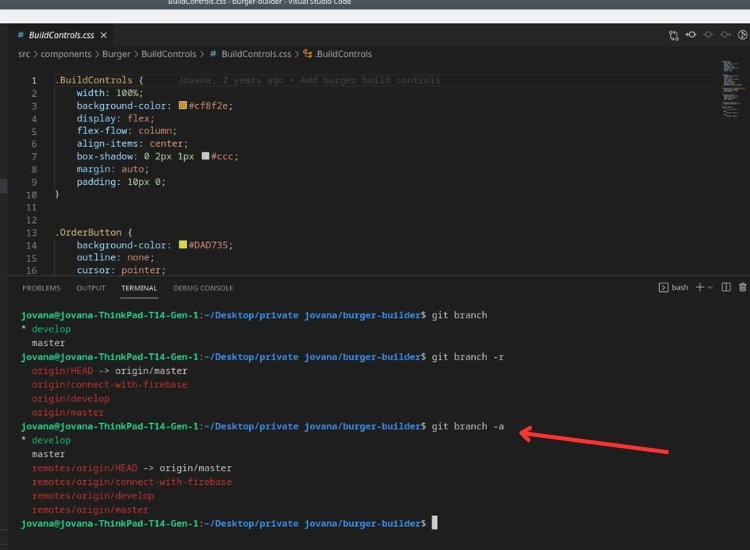
To see a comprehensive list of both local and remote branches, combine the previous two commands using the following command:
git branch -a
This command provides an overview of all branches, including both local and remote branches. Local branches will be listed without any prefixes, while remote branches will have the remote repository name prefixed.
Filtering Branches
If you have a large number of branches, finding a specific branch can be challenging.
Git provides options to filter the branch list based on specific criteria. For example, you can search for branches containing a specific term by using the following command:
git branch --list "*search_term*"
Replace “search_term” with the keyword or phrase you want to search for within branch names.
Sorting Branches
By default, Git lists branches in alphabetical order. However, you can sort the branch list based on different criteria, such as commit date or author. To sort branches by commit date, use the following command:
git branch --sort=committerdate
You can explore other sorting options by referring to the Git documentation.
Conclusion
It’s essential to have a clear understanding of both remote and local branches for effective Git branch management.
This blog post introduces useful Git commands that simplify the process of listing, viewing, and filtering branches, streamlining your development workflow. Remember to use “git branch” for local branches, “git branch -r” for remote branches, and “git branch -a” for a comprehensive list of all branches.
To enhance your branch management, explore filtering and sorting options provided by these commands. With these powerful Git tools, you can efficiently navigate and manage branches in your Git repositories.





0 Comments